Determine voltage across ![]() and
and ![]() using voltage division rule.
using voltage division rule.
Assume that
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]()
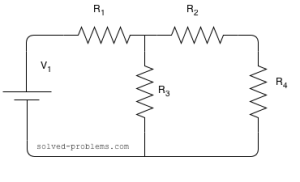
Solution:
Please note that the voltage division rule cannot be directly applied. This is to say that:
(more…)
Determine voltage across ![]() and
and ![]() using voltage division rule.
using voltage division rule.
Assume that
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]()

Solution:
Please note that the voltage division rule cannot be directly applied. This is to say that:
(more…)
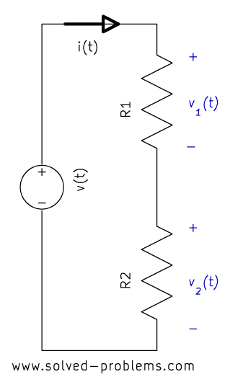
The voltage division rule (voltage divider) is a simple rule which can be used in solving circuits to simplify the solution. Applying the voltage division rule can also solve simple circuits thoroughly. The statement of the rule is simple:
Voltage Division Rule: The voltage is divided between two series resistors in direct proportion to their resistance.
It is easy to prove this. In the following circuit

the Ohm’s law implies that
![]() (I)
(I)
![]() (II)
(II)
(more…)
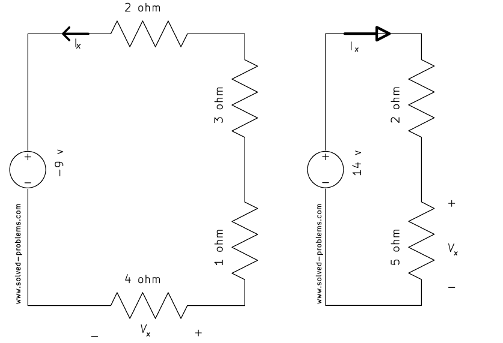
Find ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) and
) and ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) using voltage division rule.
) using voltage division rule.
a)

b)

c)

d)

Solution
a)

Voltage divider: ![]()
Ohm’s law: ![]()
(more…)