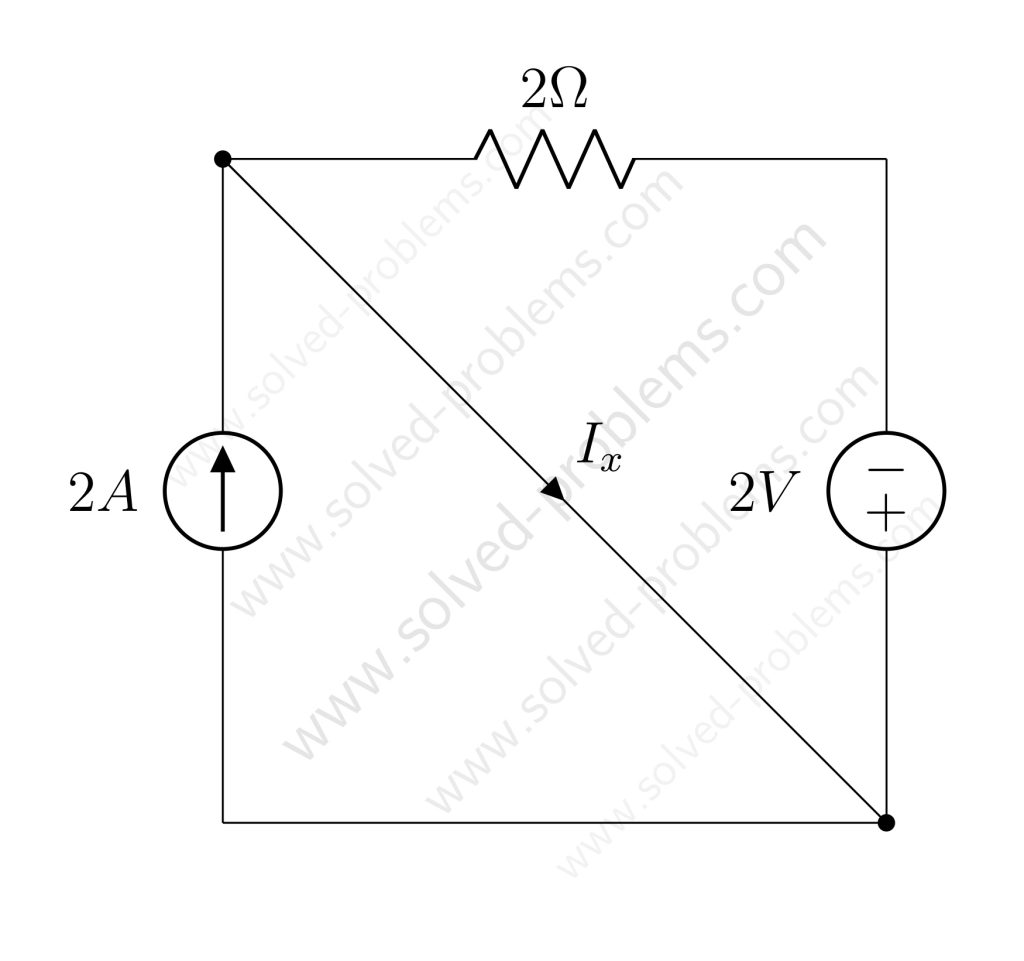
Solved the circuit to determine ![]() and power absorbed or supplied by each element.
and power absorbed or supplied by each element.
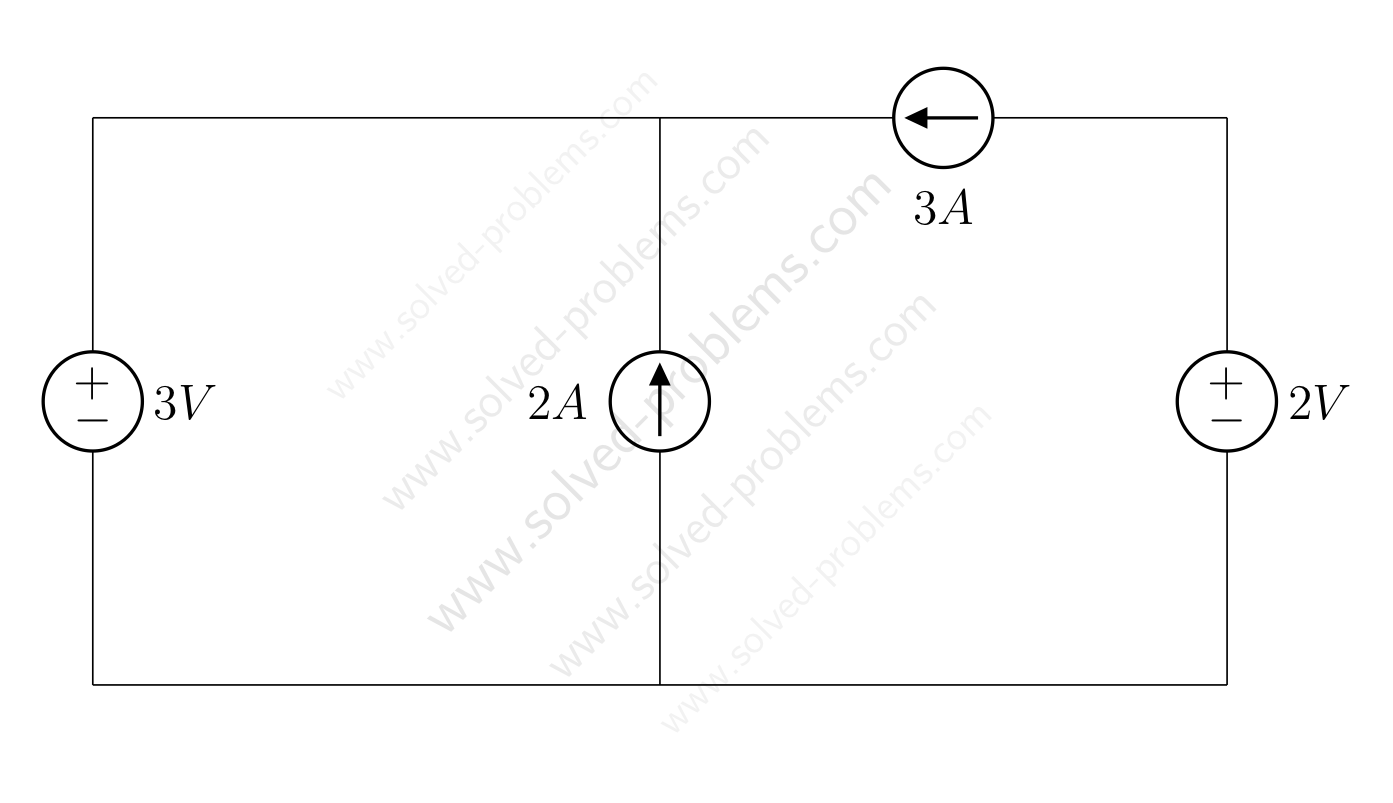
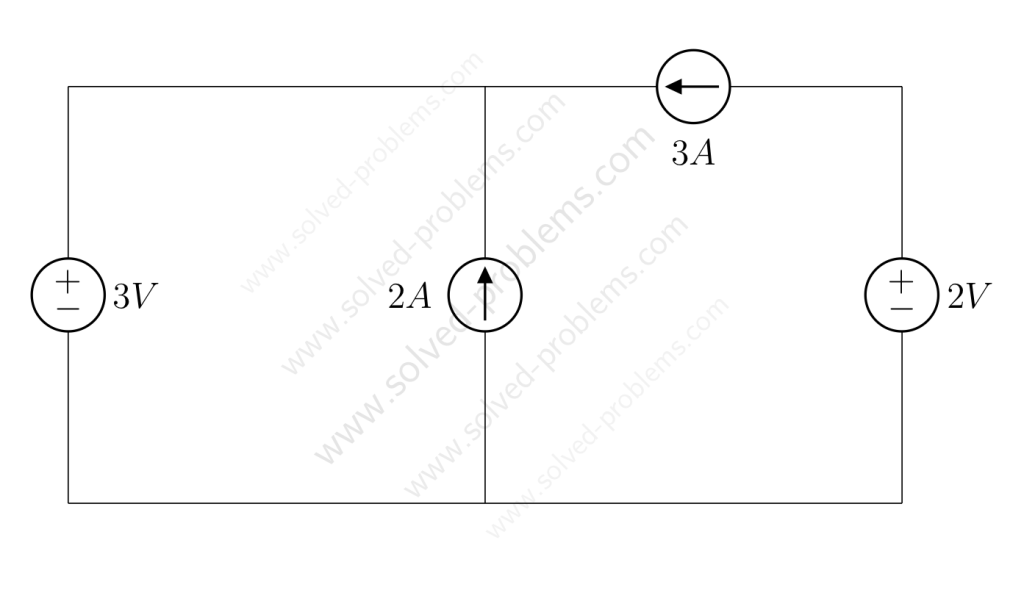
We go through solving a circuit which only containes independent sources: two voltage sources and two current sources. KVL and KCL are used to determine voltages and currents.
Determine the amount of power absorbed or supplied by each source.
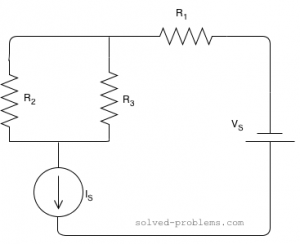
Find current of resistors, use the current division rule.

Suppose that ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution:
![]() and
and ![]() are parallel. The current of
are parallel. The current of ![]() is passing through them and it is actually divided between them. The branch with lower resistance has higher current because electrons can pass through that easier than the other branch. Using the current division rule, we get
is passing through them and it is actually divided between them. The branch with lower resistance has higher current because electrons can pass through that easier than the other branch. Using the current division rule, we get
(more…)

Solve the circuit and find the power of sources:

![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Solution:
There are three meshes in the circuit. So, we need to assign three mesh currents. It is better to have all the mesh currents loop in the same direction (usually clockwise) to prevent errors when writing out the equations.
(more…)

Find the voltage across the current source and the current passing through the voltage source.
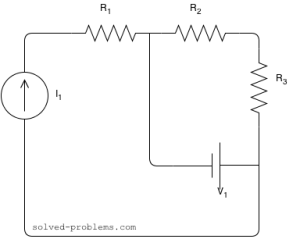
Assume that ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
Solution
![]() is in series with the current source; therefore, the same current passing through it as the current source:
is in series with the current source; therefore, the same current passing through it as the current source:
(more…)

1) Ideal Independent Voltage Sources
An ideal independent voltage source is a two-terminal circuit element where the voltage across it
a) is independent of the current through it
b) can be specified independently of any other variable in a circuit.
There are two symbols for ideal independent voltage source in circuit theory:
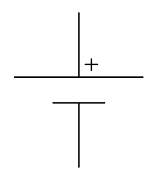
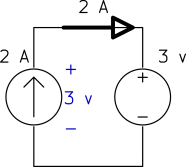
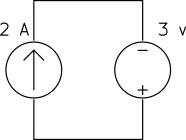
Determine the power of each source.
a)
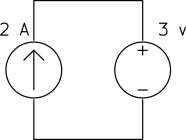
b)
Solution
a) The current source keeps the current of the loop ![]() and the voltage source keeps the voltage across the current source
and the voltage source keeps the voltage across the current source ![]() as shown below.
as shown below.
(more…)
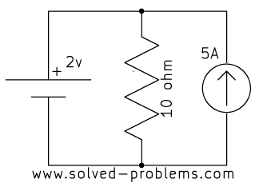
Find voltages across the current sources.
a)
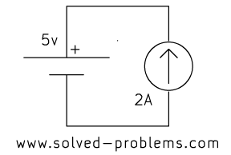
b)

c)
d)
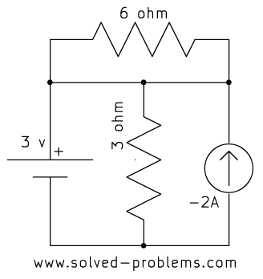
e)
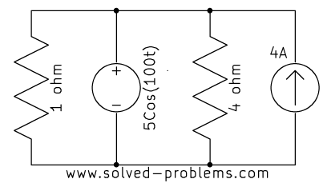
Solution
In each case, the current source is parallel with a voltage source. Therefore, the voltage across the current source is equal to the voltage of the voltage source, regardless of other elements.
(more…)
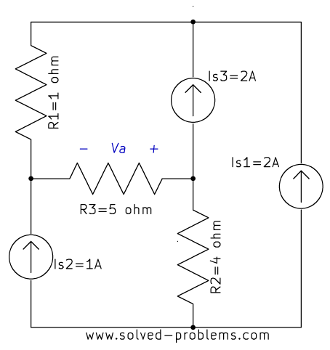
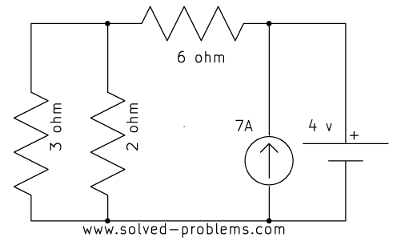
Find the power of ![]() using circuit reduction methods.
using circuit reduction methods.
Solution
![]() and
and ![]() are parallel.
are parallel. ![]() and
and ![]() are also parallel. Therefore:
are also parallel. Therefore:
(more…)
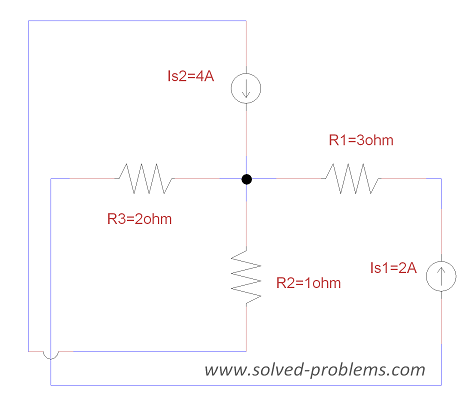
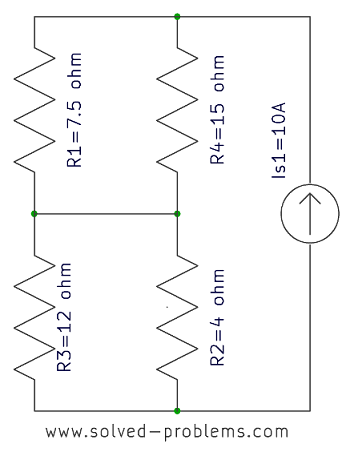
Solve the circuit using nodal analysis and find the power of ![]() .
.

Solution
a) Choose a reference node, label the voltages:
(more…)