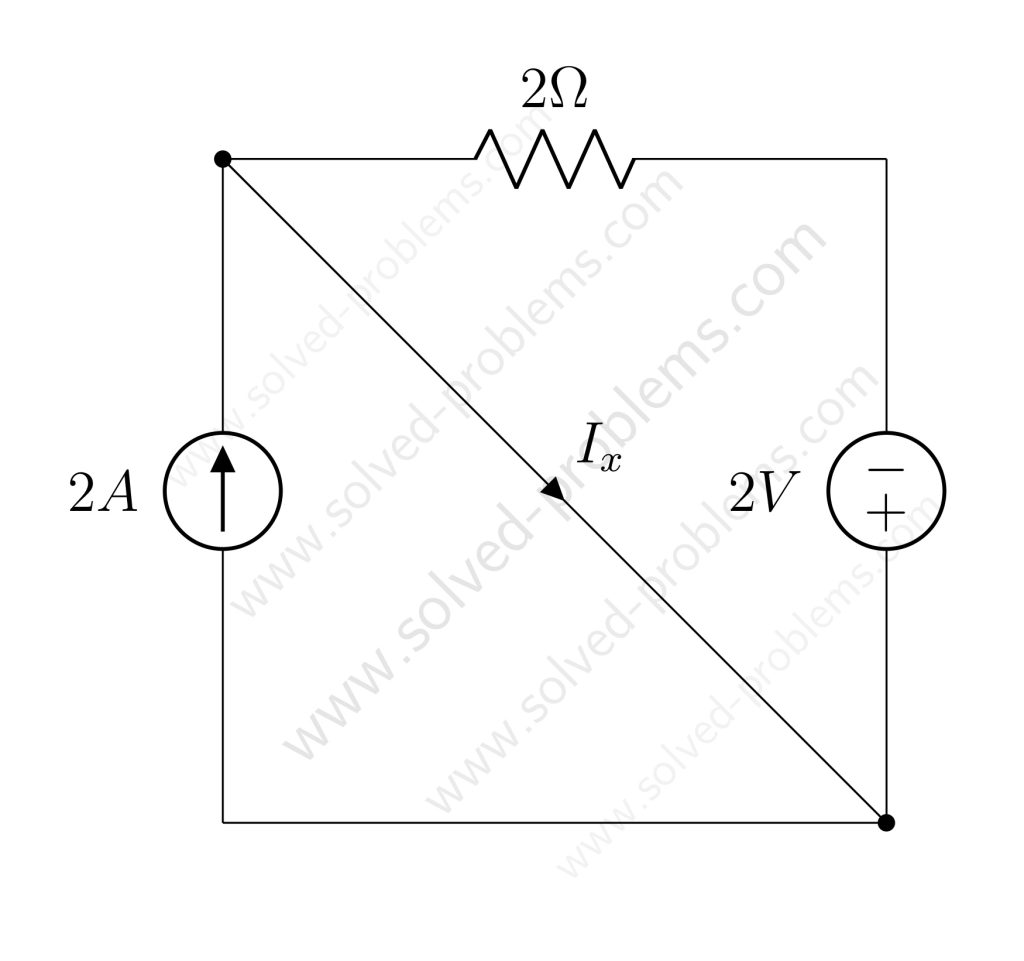
Solved the circuit to determine ![]() and power absorbed or supplied by each element.
and power absorbed or supplied by each element.
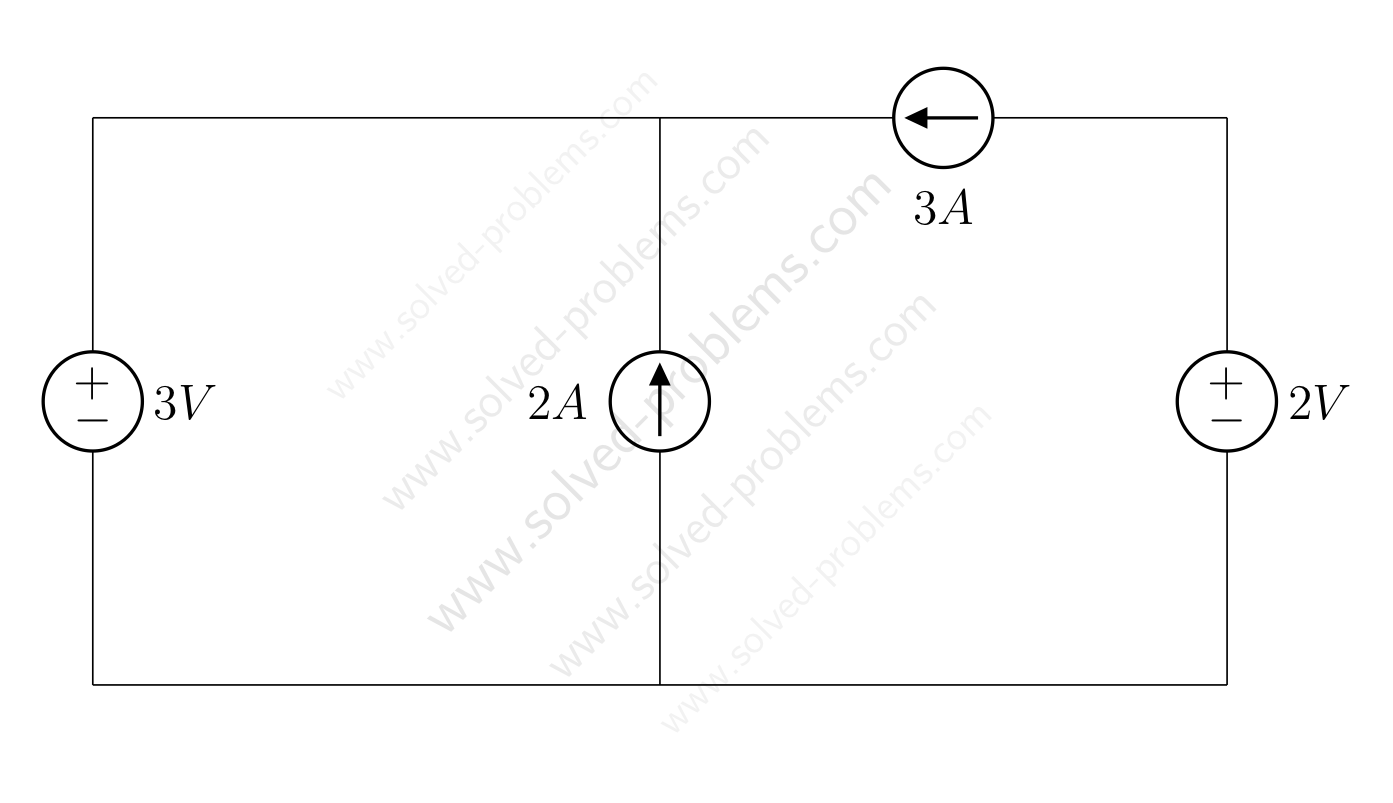
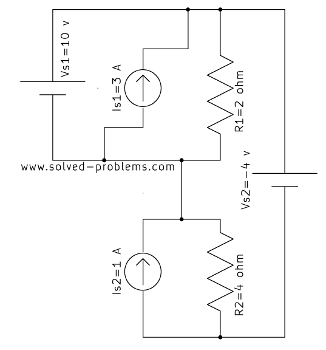
We go through solving a circuit which only containes independent sources: two voltage sources and two current sources. KVL and KCL are used to determine voltages and currents.
Determine the amount of power absorbed or supplied by each source.
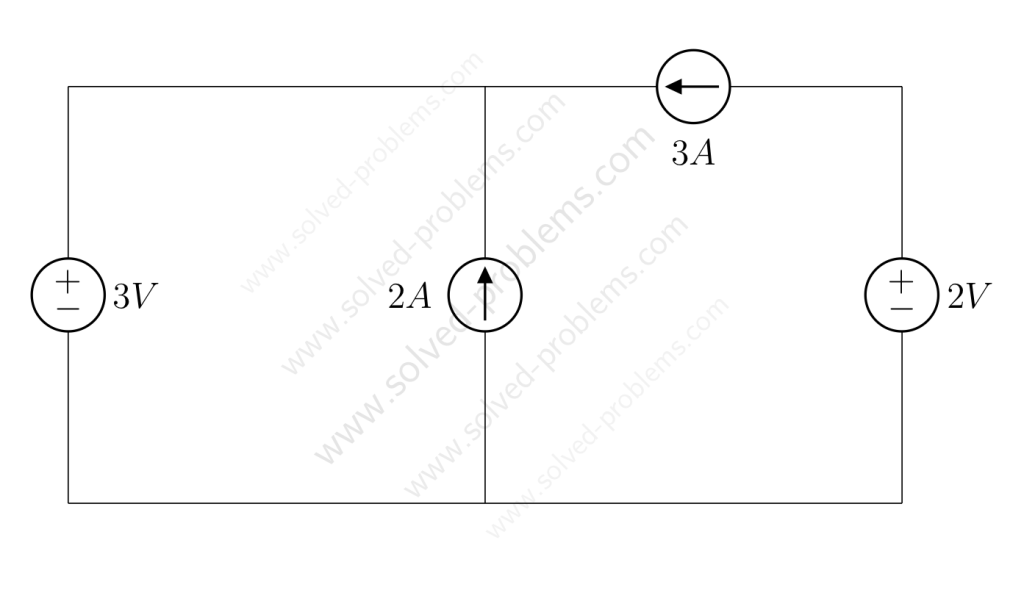
Find the voltage across the current source and the current passing through the voltage source.
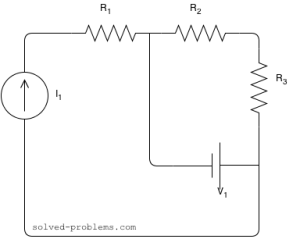
Assume that ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
Solution
![]() is in series with the current source; therefore, the same current passing through it as the current source:
is in series with the current source; therefore, the same current passing through it as the current source:
(more…)
Determine voltage across ![]() and
and ![]() using voltage division rule.
using voltage division rule.
Assume that
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]()
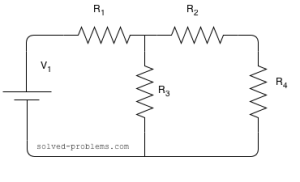
Solution:
Please note that the voltage division rule cannot be directly applied. This is to say that:
(more…)

1) Ideal Independent Voltage Sources
An ideal independent voltage source is a two-terminal circuit element where the voltage across it
a) is independent of the current through it
b) can be specified independently of any other variable in a circuit.
There are two symbols for ideal independent voltage source in circuit theory:
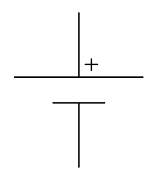
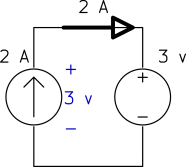
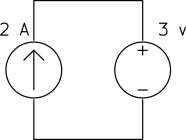
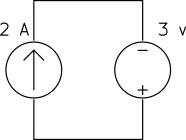
Determine the power of each source.
a)
b)
Solution
a) The current source keeps the current of the loop ![]() and the voltage source keeps the voltage across the current source
and the voltage source keeps the voltage across the current source ![]() as shown below.
as shown below.
(more…)
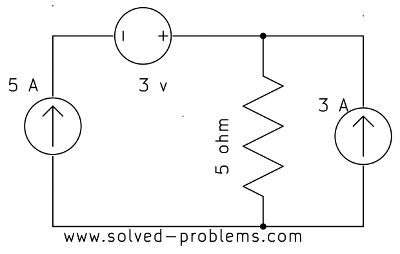
Find the current passing through the voltage source:
a)
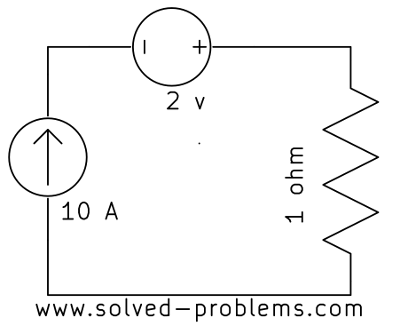
b)

Solution
a) The voltage source is in series with the current source. Since by definition a current source keeps the current passing through itself constant and the voltage source is in series with the current source, it should have the same current ![]() .
.
(more…)

Determine the power of ![]() and
and ![]() . (Hint: there is no need to use nodal analysis; voltages between nodes can be easily found by the voltage sources.)
. (Hint: there is no need to use nodal analysis; voltages between nodes can be easily found by the voltage sources.)
Solution
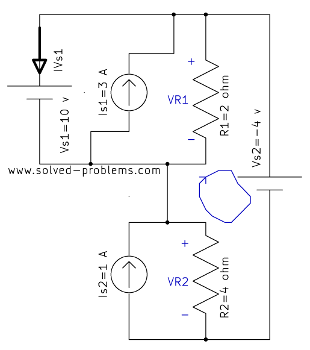
![]()
(more…)