Use nodal analysis to solve the circuit and determine the values of ![]() and
and ![]() .
.

I. Identify all nodes in the circuit.
There are four nodes in the circuit:

Use nodal analysis to solve the circuit and determine the values of ![]() and
and ![]() .
.

I. Identify all nodes in the circuit.
There are four nodes in the circuit:

Solve the circuit with the nodal analysis and determine ![]() and
and ![]() .
.

Solution
1) Identify all nodes in the circuit. Call the number of nodes ![]() .
.
The circuit has 5 nodes. Therefore, ![]() .
.
(more…)
Reference Node
In circuits, we usually label a node as the reference node also called ground and define the other node voltages with respect to this point. The reference node has a potential of ![]() by definition. The following symbol is used to indicate the reference node:
by definition. The following symbol is used to indicate the reference node:
As mentioned, the selection of the reference node is arbitrary. However, a wise selection can make the solving easier. As a general rule, it is usually chosen to be
(more…)
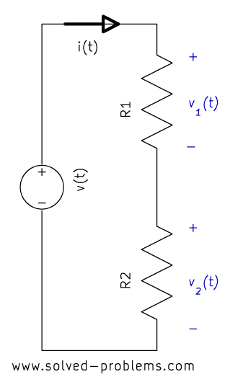
The voltage division rule (voltage divider) is a simple rule which can be used in solving circuits to simplify the solution. Applying the voltage division rule can also solve simple circuits thoroughly. The statement of the rule is simple:
Voltage Division Rule: The voltage is divided between two series resistors in direct proportion to their resistance.
It is easy to prove this. In the following circuit

the Ohm’s law implies that
![]() (I)
(I)
![]() (II)
(II)
(more…)
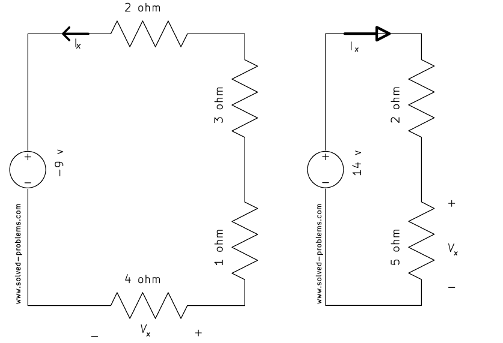
Find ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) and
) and ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) using voltage division rule.
) using voltage division rule.
a)

b)

c)

d)

Solution
a)

Voltage divider: ![]()
Ohm’s law: ![]()
(more…)

1) Ideal Independent Voltage Sources
An ideal independent voltage source is a two-terminal circuit element where the voltage across it
a) is independent of the current through it
b) can be specified independently of any other variable in a circuit.
There are two symbols for ideal independent voltage source in circuit theory:
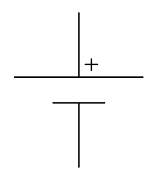
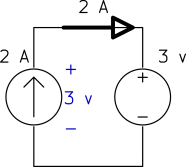
Determine the power of each source.
a)
b)
Solution
a) The current source keeps the current of the loop ![]() and the voltage source keeps the voltage across the current source
and the voltage source keeps the voltage across the current source ![]() as shown below.
as shown below.
(more…)
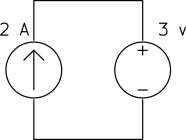
Find the current passing through the voltage source:
a)
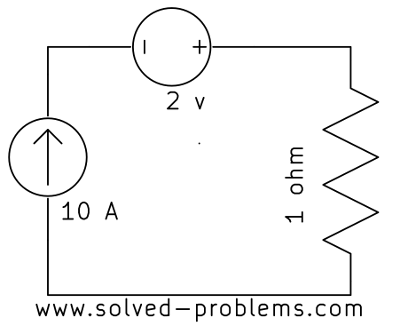
b)

Solution
a) The voltage source is in series with the current source. Since by definition a current source keeps the current passing through itself constant and the voltage source is in series with the current source, it should have the same current ![]() .
.
(more…)
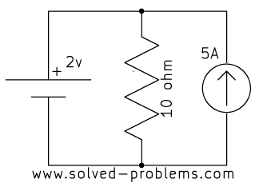
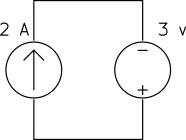
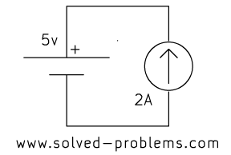
Find voltages across the current sources.
a)
b)

c)
d)
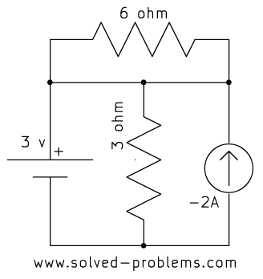
e)
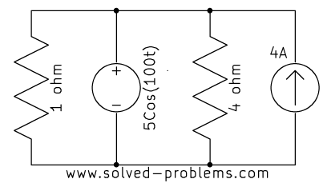
Solution
In each case, the current source is parallel with a voltage source. Therefore, the voltage across the current source is equal to the voltage of the voltage source, regardless of other elements.
(more…)

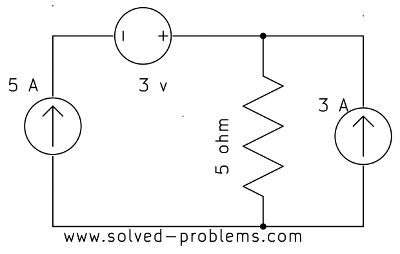
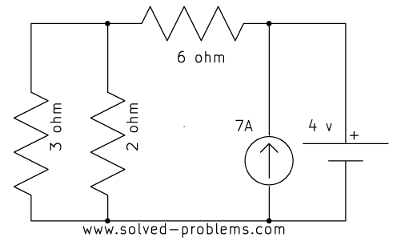
Determine the power of ![]() and
and ![]() . (Hint: there is no need to use nodal analysis; voltages between nodes can be easily found by the voltage sources.)
. (Hint: there is no need to use nodal analysis; voltages between nodes can be easily found by the voltage sources.)
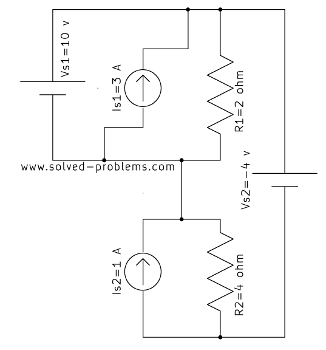
Solution
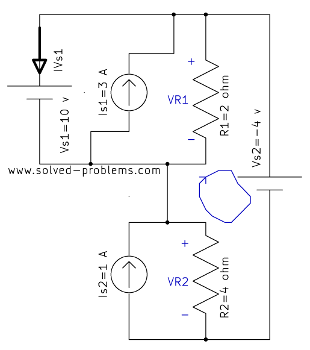
![]()
(more…)