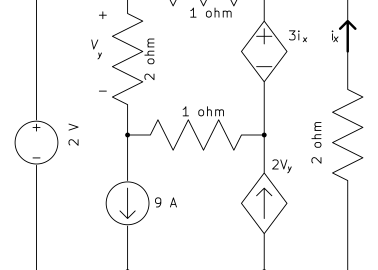
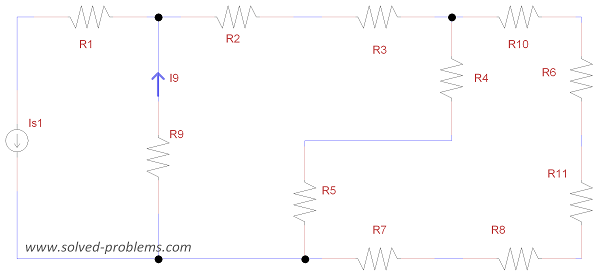
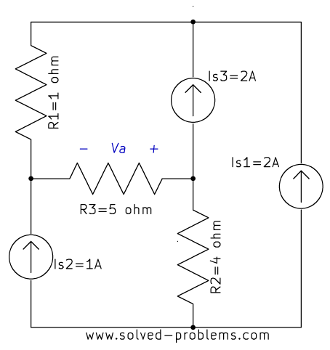This is a complicated nodal analysis problem. The circuit has two independent sources and two dependent sources. A supernode is formed to solve the problem.
Category Archives: Resistive Circuits
Problem 1-16: Voltage Divider
In this solved problem, four circuits are solved using voltage divider (the voltage division rule). Problems are arranged from simple ones to more challenging ones. It is shown how voltage divider can be used to solve simple problems.
Problem 1-12: Using Voltage Sources to Determine Node Voltages
A three-node circuit is solved by using the voltage of voltage sources. The nodal analysis is not used since there are enough voltage sources to determine all node voltages.
Problem 1-11: Solving a Circuit with Three Nodes by the Nodal Analysis
The circuit is solved using the Nodal Analysis. It has three nodes, two sources (one voltage, one current, both independent) and four resistors.
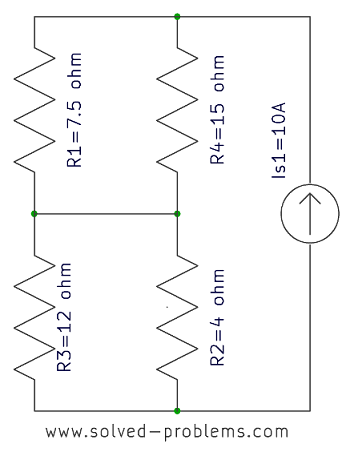
Problem 1-10: Solving by Nodal Analysis – Circuit with Four Nodes
A circuit with four nodes solved using the Nodal Analysis. Step-by-step solution is provided. The circuit has three current sources and three resistors.
Problem 1-9: Power of a Current Source
A simple DC resistive circuit is solved by circuit reduction (for series and parallel resistors) and the power a current source calculated.
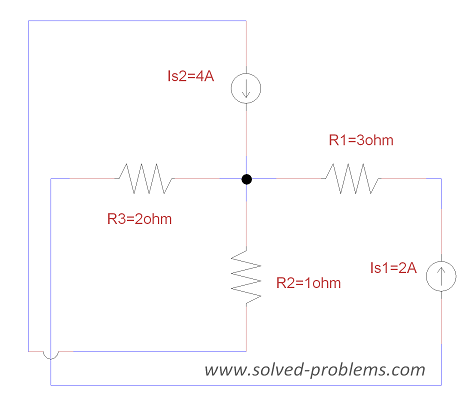
Problem 1-8: Nodal Analysis – Power of Current Source
A simple DC resistive circuit with three resistors and two current sources are solved by the Nodal Analysis and power of one current source is determined.
Problem 1-7: Circuit Reduction – Current Divider
Solving a circuit by using circuit reduction and current divider methods
Problem 1-6: Single Node-Pair Analysis
Solving a circuit with single node-pair analysis without reducing it.
Problem 1-5: Single Loop Analysis
Solving circuit with single loop analysis without reducing